Description of the MSCP Study Area
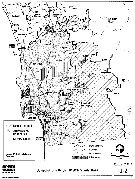
The MSCP study area covers approximately 900 square miles (582,243 acres) in southwestern San Diego County and includes the City of San Diego, portions of the unincorporated County of San Diego, ten additional city jurisdictions, and several independent special districts (Figure 1-2). The study area is bordered by Mexico to the south, National Forest lands to the east, the Pacific Ocean to the west and the San Dieguito River Valley to the north. Naval Air Station Miramar, the Point Loma Naval Complex, and other military lands are within the MSCP study area but are being planned separately.
Vegetation Communities and Evaluated Species

Approximately 54% (315,940 acres) of the MSCP study area supports several distinct vegetation communities or habitat types, most of which are considered sensitive or rare, with the remainder developed (41%) or in agriculture (5%). The MSCP preserve was designed using an evaluation of 93 species as indicators of the range of habitats and biological diversity in the study area. Included within the 93 species were 41 species that are federally or state listed, candidates for listing, or proposed for listing. The plan attempts to maximize the presence of these species and their habitats in the preserve.
Biological Core and Linkage Areas
Biological core and linkage areas were identified to assist local jurisdictions and special districts as one element to be considered in identifying their portion of the MSCP preserve and/or preserve design criteria. The most critical biological resources were prioritized for preservation to maximize the conservation value of the preserve, to efficiently use acquisition funds and to identify less important habitat areas that could be developed. Sixteen core biological resource areas and associated habitat linkages, totaling approximately 202,757 acres of habitat, were identified. Subarea plans with specific preserve boundaries maximize inclusion of unfragmented core areas and linkages in their preserve design to the extent possible.
Ownership
The study area contains 315,940 acres of habitat with almost two-thirds (about 194,563 acres) being privately owned. Over one-third of the habitat is in military (20,082 acres) or other public ownership (101,295 acres).
Gap Analysis of Habitat Protection and Planned Land Uses
A gap analysis was performed to identify where existing protection of key biological resources was already in place (such as planned open space lands, public lands and lands unlikely to be developed because of steep slopes and floodplains) and where "gaps" in habitat protection may occur. The gap analysis showed that only 17% of the biological core and linkage areas was already preserved for biological open space as of 1994, and these protected areas were widely distributed without linkages between them. According to adopted general and community plans, most of the remaining habitat areas in the MSCP study area are planned to be developed with low density residential uses (39%) or used as parks, preserves or open space (29%). The local jurisdictions considered these planned land uses in designing or establishing criteria for the MSCP preserve and will amend land use plans, as needed, to implement the MSCP (see Section 5).
Figure 1-2, Jurisdictions Within MSCP Study Area
View Larger Image
Future Growth
In allocating future forecast growth in the region, the local jurisdictions and SANDAG found that, without the MSCP, the existing general and community plans would accommodate residential growth up to around 3.3 million people, which is forecast to be reached in 2005. It is projected that after 2005, there will not be sufficient vacant land designated by the general and community plans for residential use at urban densities (more than one dwelling unit per acre). In response to this issue, local jurisdictions have been working with SANDAG to formulate a Regional Growth Management Strategy to accommodate residential growth beyond 2005 by focusing growth around major transit services, providing mixed uses at community centers and locating residences within major employment centers. Although a lack of sufficient residentially designated lands in land use plans would occur with or without a habitat preserve system, habitat conservation and a new growth management strategy can be mutually supportive of quality of life objectives and the need for economic growth.